
UPF stands for Ultraviolet Protection Factor, which is a measurement of the sun protection strength of clothing and fabrics used in outdoor shades (e.g. umbrellas, shade sails, pavilions, awnings and screened-in porches). It represents the ratio of UV radiation exposure with and without the protection of the measured textile.
What does UPF mean?
There are many factors that go into the calculation of UPF ratings, but at the end of the day you probably just want to understand what the numbers indicate. You might want to know, “what is UPF 50?” In this example, a fabric with UPF 50 will permit only 1/50th (2%) of ultraviolet radiation to pass through it.
What is a good UPF rating?
Obviously, the higher the UPF the stronger the protection against the sun. However, there are levels of protection that you should be aware of as you evaluate textiles for patio umbrellas, shades and outdoor clothing [Bilimis 2011].
Levels of UPF Protection
| UVR Protection | UPF Rating | UVR % |
|---|---|---|
| Moderate | 10 to 19 | 10 to 5.1 |
| High | 20 to 29 | 5.0 to 3.4 |
| Very High | 30 to 49 | 3.3 to 2.0 |
| Maximum | 50+ | <2.0 |
What’s the difference between SPF and UPF?
SPF stands for Sun Protection Factor, which is used to measure the effectiveness of sunscreen and other products. It is a time-related measurement relative to your skin’s natural tendency to burn. A sunscreen with an SPF rating of 30 provides 30 times more protection against UVB rays than if you wore no sunscreen at all. So, if you have fair skin and tend to burn after 10 minutes, applying SPF 30 sunscreen will allow you to be exposed for up to 300 minutes without burning. As mentioned above, UPF measures the UVA and UVB radiation that penetrates a textile and reaches the skin.
What’s the difference between UVA and UVB radiation?
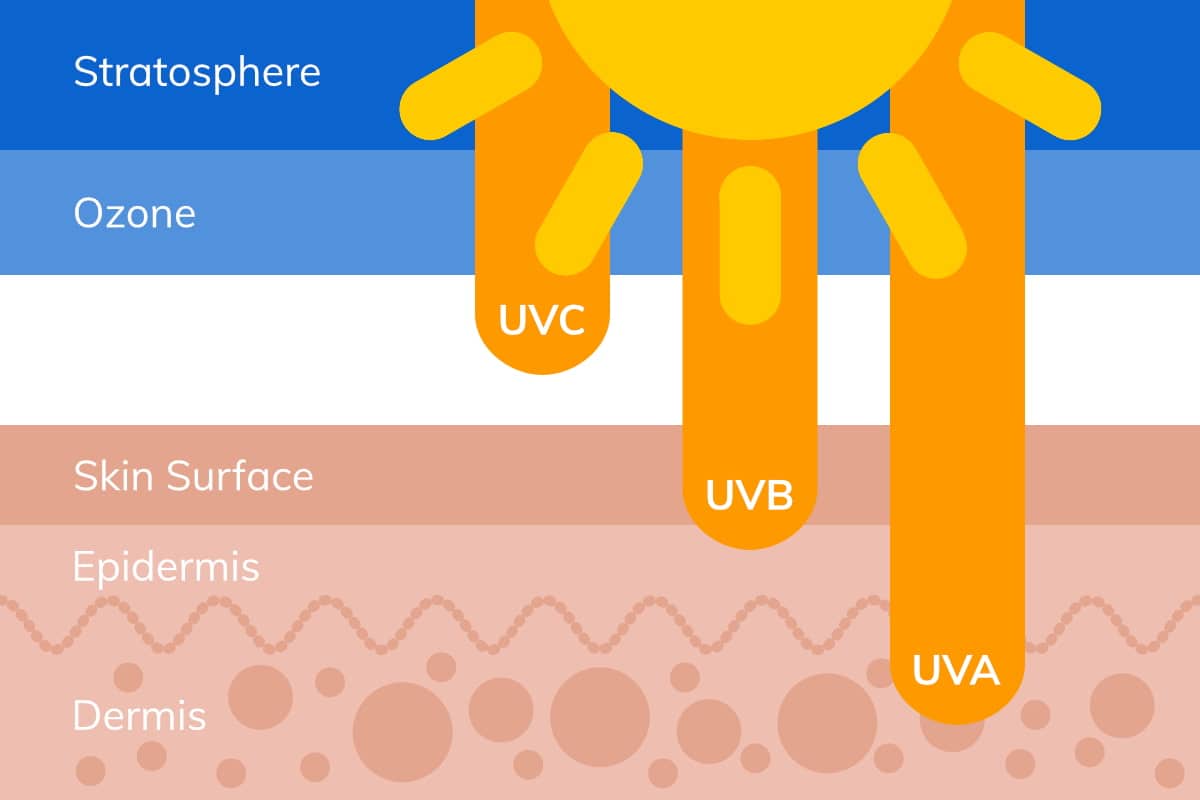
- UVA rays account for nearly 95% of the ultraviolet radiation that reaches the earth’s surface. They penetrate deep into the skin’s dermis and can lead prematurely age the skin, cause wrinkles and suppress the immune system. Recent studies have shown that UVA rays also damage skin cells in the lower layer of the epidermis, where most skin cancers develop. These rays can penetrate cloud cover and glass.
- UVB rays are more intense, but far less prevalent than UVA rays. They are the primary cause of skin reddening, sunburn and other superficial damage to the skin’s outer epidermal layer (e.g. tanning, photo-aging, etc). UVB radiation plays a significant role in the onset of skin cancer. These rays do not penetrate glass to any measurable degree, but they do bounce off of reflective surfaces, so they can burn you when you are under cover or during icy winter months.
[Soter 2017]
Origin of Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) ratings
Clothing designed specifically to block ultraviolet light started being produced in the 1990s. It was prevalent in Australia as an alternative or addition to sunscreen lotions and sprays. Research by swimwear companies led to the establishment of lab-tested Australian standards for UV protective textiles by ARPANSA. Their UPF rating system evolved into more rigorous American standards set by the ASTM, which also considers various durability criteria in its testing protocols.
ARPANSA – Australian Radiation Protection & Nuclear Safety Agency
This organization conducts research, establishes standards and advises the Australian government on the risks and responses to radiation and nuclear safety. For more information, visit the ARPANSA website.
ASTM – American Society for Testing & Materials
This internationally recognized organization is comprised of more than 30,000 technical experts from around the world. Through their collaborative efforts, they establish testing methodology, classifications, global standards and best practice guides to improve product quality and enhance health and safety. Learn more by visiting the ASTM website.
What characteristics affect a fabric’s UPF?
This is an important question to answer because we all have preconceived notions about what is appropriate to wear during the summer. Lightweight white see-through fabric shirts may allow a breeze to cool your skin in the heat, but are they really the best sun protective clothing to wear? UPF clothing and patio umbrella canopies are more than just their aesthetics.
- Weave – The tighter the fabric is woven together, the less UV radiation passes through
- Color – Dark colors of identical fabric types absorb ultraviolet rays more strongly than their lighter shades, which increases the sun protection
- Weight – A heavier version of the same fabric will be minimally more protective against UVR
- Stretch – The greater the stretch or tension put on a textile, the lower the UPF rating
- Water – Some fabrics, such as polyester and cotton, provide less protection against UVR when they have absorbed water
- Washing – Cotton-based fabrics tend to shrink after the first washing, thereby tightening the weave and reducing the transmitted ultraviolet radiation
- Additives – UVR stabilizers or additives can be used to improve the sun protection of a variety of textiles
[Gies, Roy, Toomey, & McLennan 1998]
Relative UV protection of outdoor textiles
Fabrics have varying degrees of inherent ultraviolet protection, regardless of common characteristics. Viscose and silk, for example, are more UV protective than other fabrics when wet, which could be reduced as much as fifty percent. Polyester absorbs UV light without additives, unlike other textiles that require them during manufacturing.

Patio umbrella UV protection
Outdoor umbrellas, awnings and shade sails provide protective barriers between harmful UV radiation from direct sunlight and your skin. However, they do not prevent scattered or indirect rays that bounce off surrounding surfaces and objects. Comparatively speaking, using sunscreen with SPF 100 is more effective than a beach umbrella under the same conditions and timeframe. It should be noted, however, that neither prevents sunburn completely. This highlights the importance of employing a combination of protection methods to provide maximum UV protection [Ou-Yang 2017].
Premium brands producing UV-resistant fabrics for shade canopies
Most high-quality patio umbrella canopies and sunshades are made with heavy furniture or awning-grade solution-dyed textiles to resist fading. Acrylic and polyester are the most common fabrics used due to their strength and weather resistance. However, olefin is more eco-friendly and polyethylene may offer cooling benefits.
- Sunbrella (Acrylic) – 98% UV protection & Greenguard & Skin Cancer Foundation certified
- Outdura (Acrylic) – UPF 50+ & OEKO-TEX certified
- Pacifica (Polyester) – UPF 40
- Texsilk (Olefin) – UPF 80 & OEKO-TEX certified. Eco-friendly – 100% recyclable
- Coolaroo (Polyethylene) – 90% UV protection

Popular clothing brands specializing in UV-protective fabrics
Clothing must be graded as UPF 50 or better to be considered protective against UV rays. Manufacturers typically weave a blend of complementary textiles to take advantage of each fabric’s unique characteristics and add UV absorbers throughout the process. Elastane (a.k.a. Spandex) is frequently used for active and athleisure wear, while bamboo viscose is added to clothing intended to get wet. Cotton and polyester provide strength for UPF garments requiring less stretch.
- Coolibar – Develops the most technical, elegant wearable sun protection and is the first clothing company to receive The Skin Cancer Foundation’s Seal of Recommendation
- Mott50 (owned by Coolibar) – Fusion of sun-protective fashion & elegant style
- Solbari – Provides high-quality, lightweight & breathable sun protective clothing, sun hats & accessories
- Cabana Life – Founded by a skin cancer survivor, they strive to prevent skin cancer with stylish, sun-safe solutions
Frequently Asked Questions – UPF
Is UPF better than SPF?
It’s difficult to say which is better because UPF and SPF measure different things and actually work together to protect your skin (covered up and exposed) from harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun. The Ultraviolet Protection Factor measures the effectiveness of your clothing or shade at stopping UV rays from reaching your skin, while the Sun Protection Factor rates a sunscreen’s ability to extend the time you can be in the sun without burning.
What color is best for sun protection?
All other characteristics being equal, fabrics that are darker or more vivid in color absorb UV radiation more than lighter or paler ones. The more a fabric absorbs ultraviolet rays, the more sun protection it provides. A bright yellow patio umbrella canopy is more protective than a pale one.
Additional Resources
References
- Bilimis, Z. (2011). Measuring the UV protection factor (UPF) of fabrics and clothing.
- Soter, N. A. (2017). Acute effects of ultraviolet radiation on the skin. In Clinical Photomedicine (pp. 75-93). Routledge.
- Gies, P. H., Roy, C. R., Toomey, S., & McLennan, A. (1998). Protection against solar ultraviolet radiation. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 422(1), 15-22.
- Ou-Yang, Hao, et al. “Sun protection by beach umbrella vs sunscreen with a high sun protection factor: a randomized clinical trial.” JAMA dermatology 153.3 (2017): 304-308.





Leave a Reply